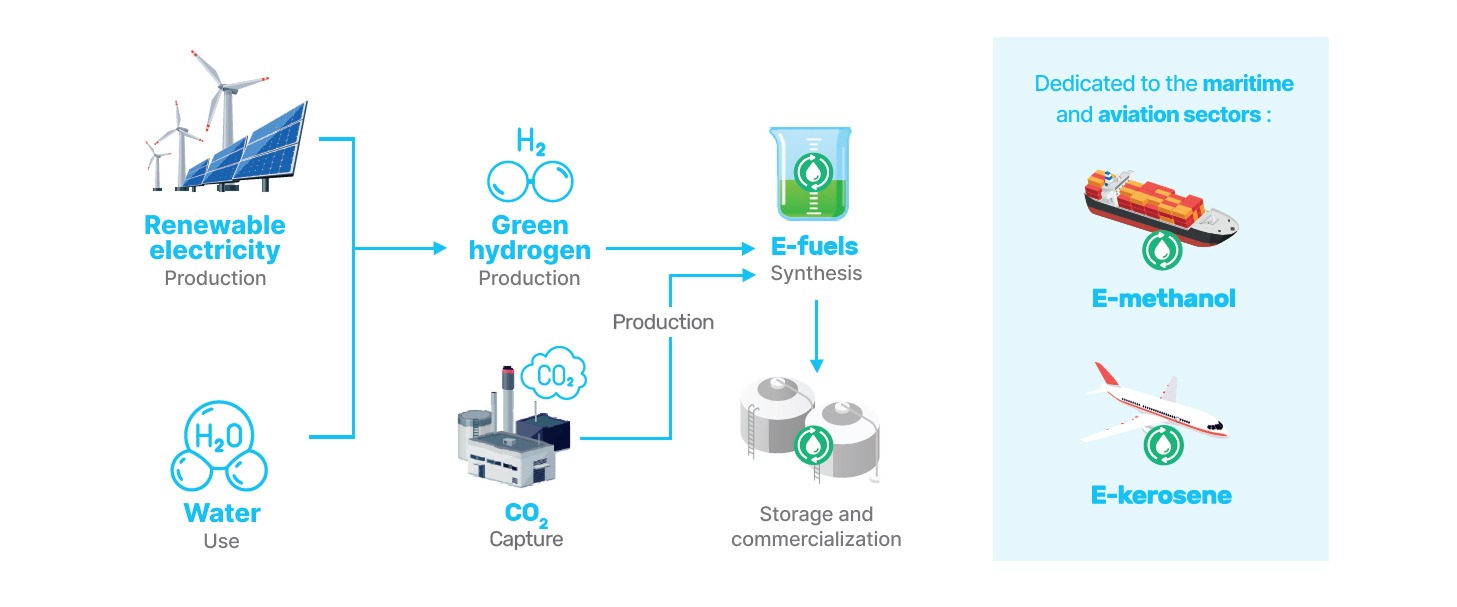
What are e-Fuels?
Synthetic fuels for low-carbon transport
By recycling the CO2 present in the air or in the smoke, this new generation of fuels will make it possible to avoid at least 70% of greenhouse gas emissions. Some 27,000 aircraft and 90,000 ships around the world are set to use these low-carbon fuels, such as e-methanol and e-kerosene, as future substitutes for fossil fuels.
Who are we?
A key player in the decarbonization of maritime and air transport
- Contribute to the decarbonization in the maritime and air transports
- To develop, finance, build and operate sustainable fuel production plants worldwide,
- Market e-fuels that will significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions
member of:
Our sectors
Maritime
Today, maritime freight accounts for 11% of global transport-related greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. To curb this trend, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has adopted the "2023 Strategy" for reducing GHG emissions from ships. Its goal is to cut CO₂ emissions from international maritime transport by at least 40% by 2030 and achieve net-zero GHG emissions by 2050 or earlier.
Today, maritime freight accounts for 11% of global transport-related greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. To curb this trend, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has adopted the "2023 Strategy" for reducing GHG emissions from ships. Its goal is to cut CO₂ emissions from international maritime transport by at least 40% by 2030 and achieve net-zero GHG emissions by 2050 or earlier.
Aviation
The aviation sector accounts for 2 to 3% of global CO₂ emissions. Sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) are a promising alternative to fossil fuels but currently represent only 1% of total volumes. In response, the European Parliament adopted the "Refuel EU" legislation in September 2023, setting a minimum SAF requirement of 2% in aircraft fuel tanks by 2025. This threshold will gradually increase to reach 70% by 2050. Similarly, at COP28, around 100 countries committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions from aviation by at least 5% by 2030.
The aviation sector accounts for 2 to 3% of global CO₂ emissions. Sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) are a promising alternative to fossil fuels but currently represent only 1% of total volumes. In response, the European Parliament adopted the "Refuel EU" legislation in September 2023, setting a minimum SAF requirement of 2% in aircraft fuel tanks by 2025. This threshold will gradually increase to reach 70% by 2050. Similarly, at COP28, around 100 countries committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions from aviation by at least 5% by 2030.
Decarbonising maritime and air transport
Our projects
Project Janassim: an E-Fuel Production Plant in Morocco
As part of the Morocco Green Hydrogen Offer published in March 2024, our subsidiary MGH Energy Maroc is leading the ambitious Janassim project to develop, build and operate a plant to produce renewable synthetic fuels in the Dakhla-Oued Ed-Dahab region. As a player in the decarbonisation of maritime and air transport, MGH Energy Maroc intends to contribute to the emergence of sustainable energy sovereignty in the Kingdom. In addition to the Janassim plant, the company's project is part of an integrated approach that includes the development of associated industrial activities, the introduction of training and specialised diplomas tailored to emerging needs, and the deployment of initiatives to support agriculture and the local economy.
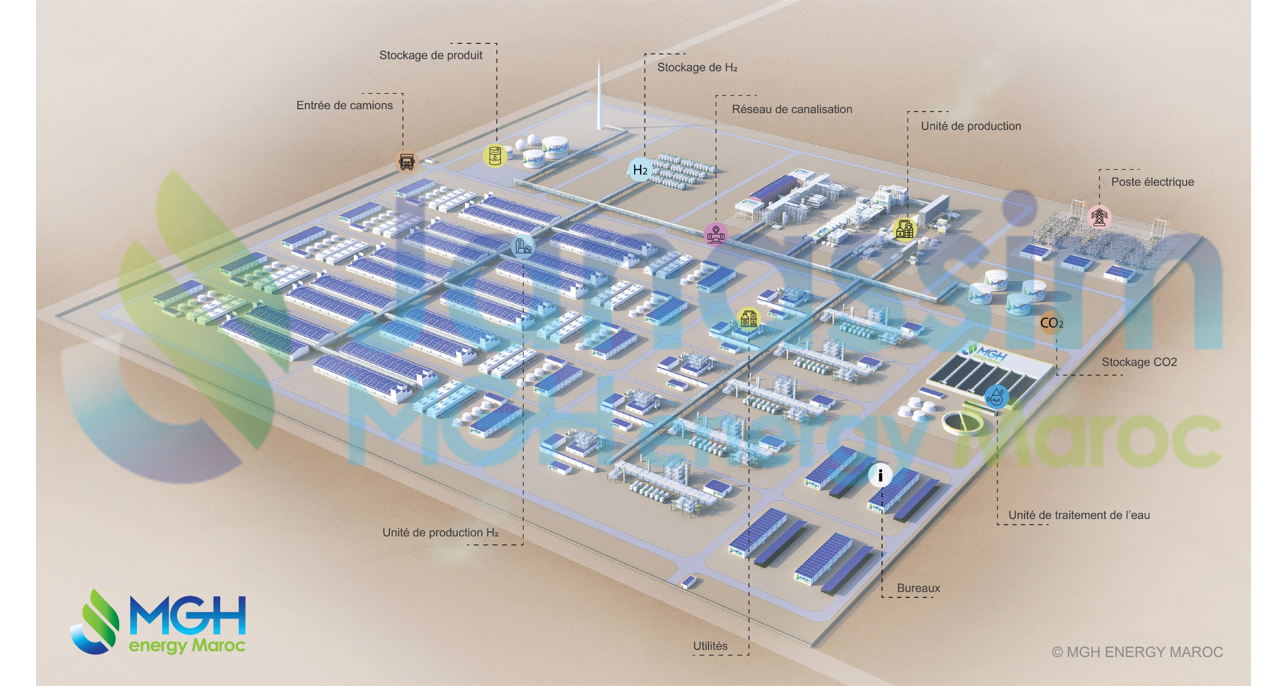
Janassim in figures:
- Nearly 500,000 tonnes/year of renewable fuels (e-methanol and e-jet)
- 2.2 GW of renewable energy (wind and photovoltaic)
- 50 billion Moroccan dirhams of investment
- 2,600 jobs created over 30 years of operation
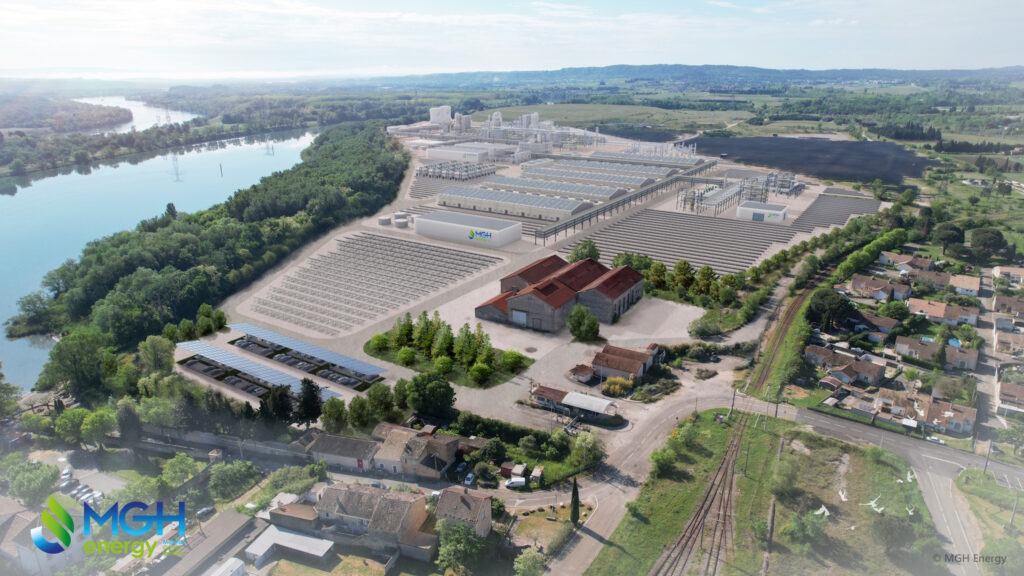

L'Ardoise in figures :
- Location: Laudun-l'Ardoise (Gard)
- Target production: up to 70,000 tonnes/year of e-kerosene and 50,000 tonnes/year of e-methanol from 2031.
- Investment: €1 billion
- Jobs: 400 direct jobs during the construction phase (2028-2031) and 200 permanent jobs during operation
L'Ardoise project: a synthetic fuels production plant in France
On 10 February 2026, the Communauté d'Agglomération du Gard Rhodanien announced the selection of the synthetic fuels production project led by MGH Energy, as part of the conversion of the L'Ardoise industrial site (Laudun-l'Ardoise). The aim of the project is to build a production unit for sustainable synthetic fuels to contribute to the decarbonisation of air (e-kerosene) and sea (e-methanol) transport. Industrial commissioning is scheduled for 2031.
Located on a plot of land that has been awarded the « turnkey site - France 2030 label », the project benefits from a strategic location and multimodal infrastructure (river, rail, pipeline) guaranteeing flexibility and logistical efficiency. Priority will be given to river transport, with barge transport via the Rhône and a connection to the Fos-sur-Mer axis.
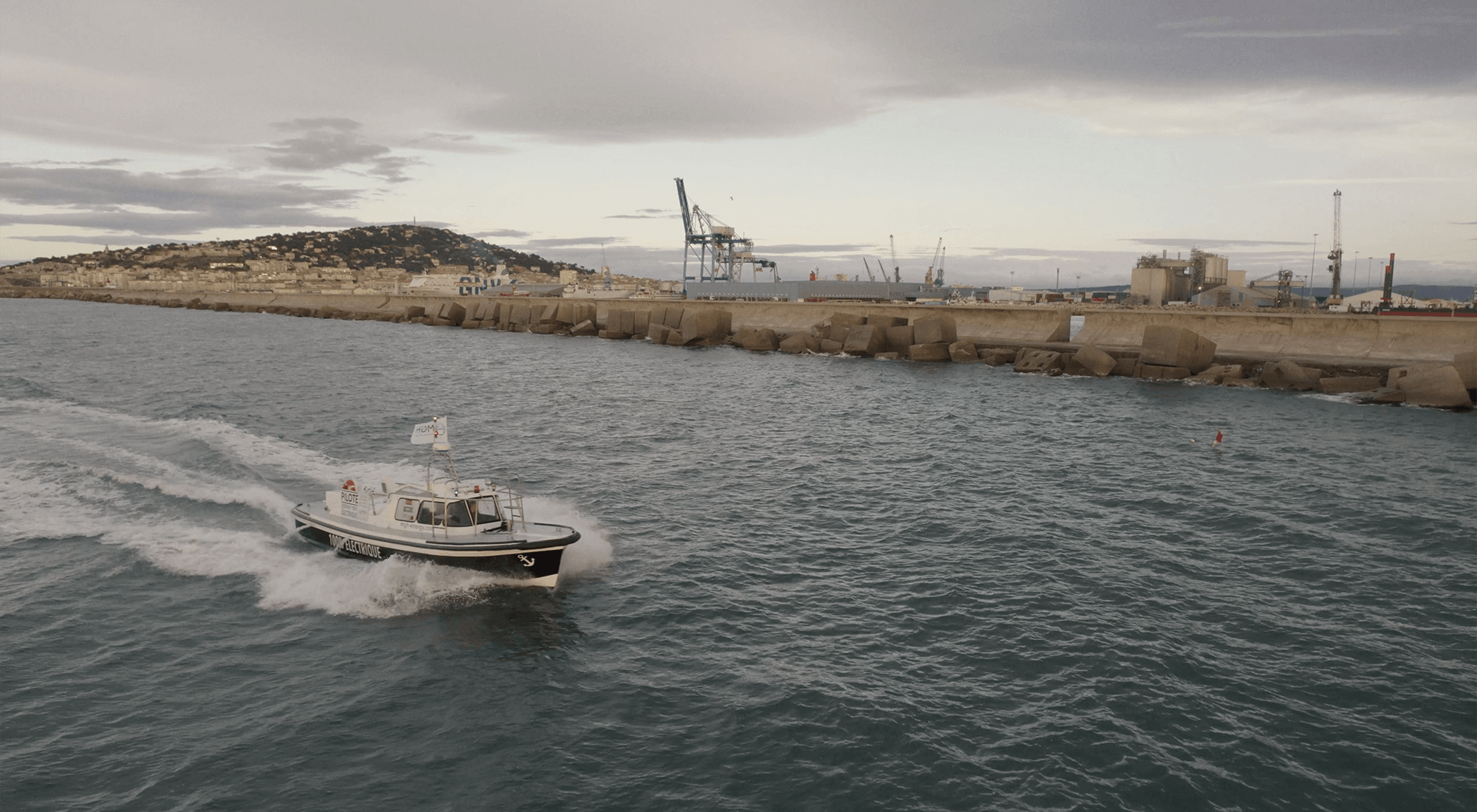
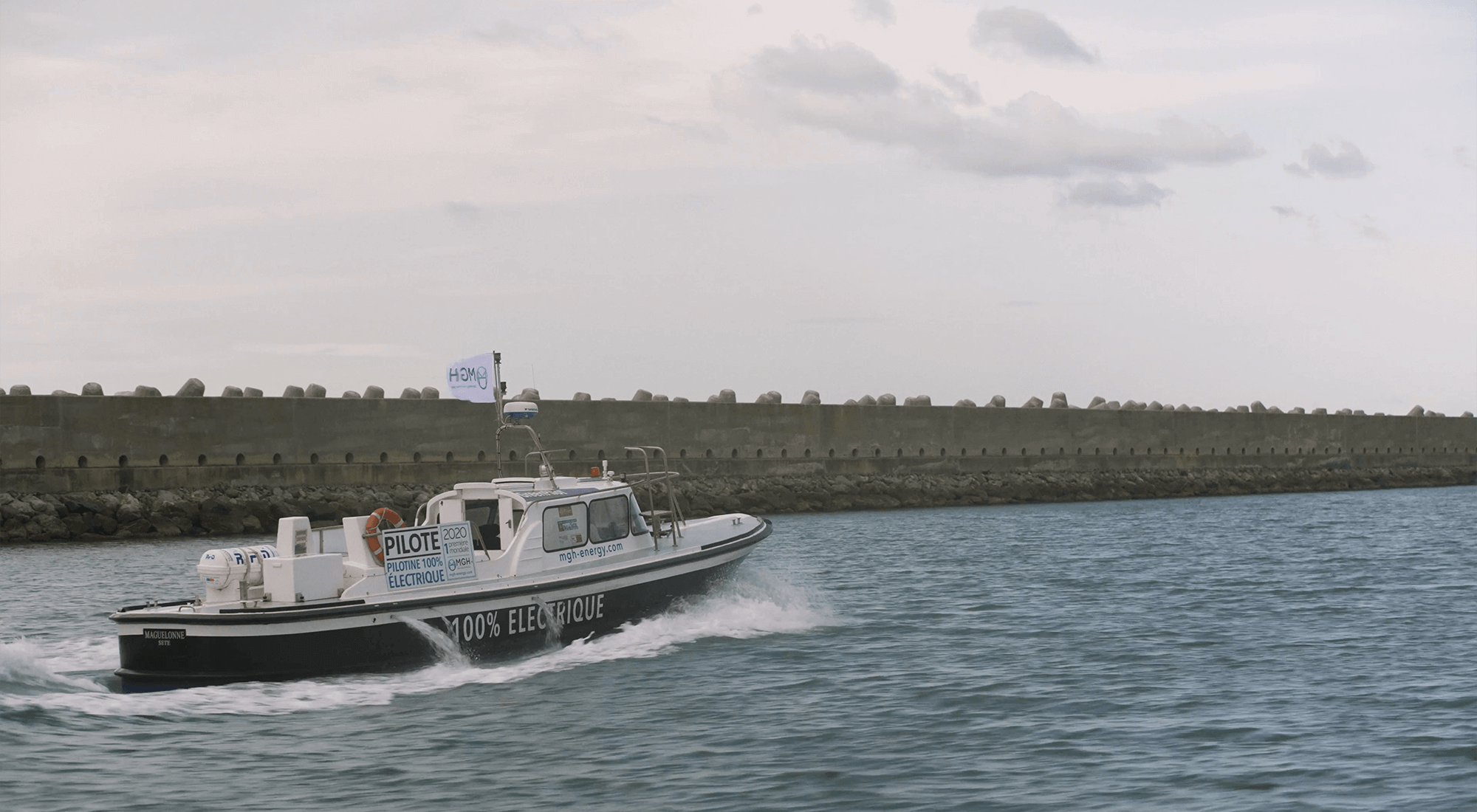
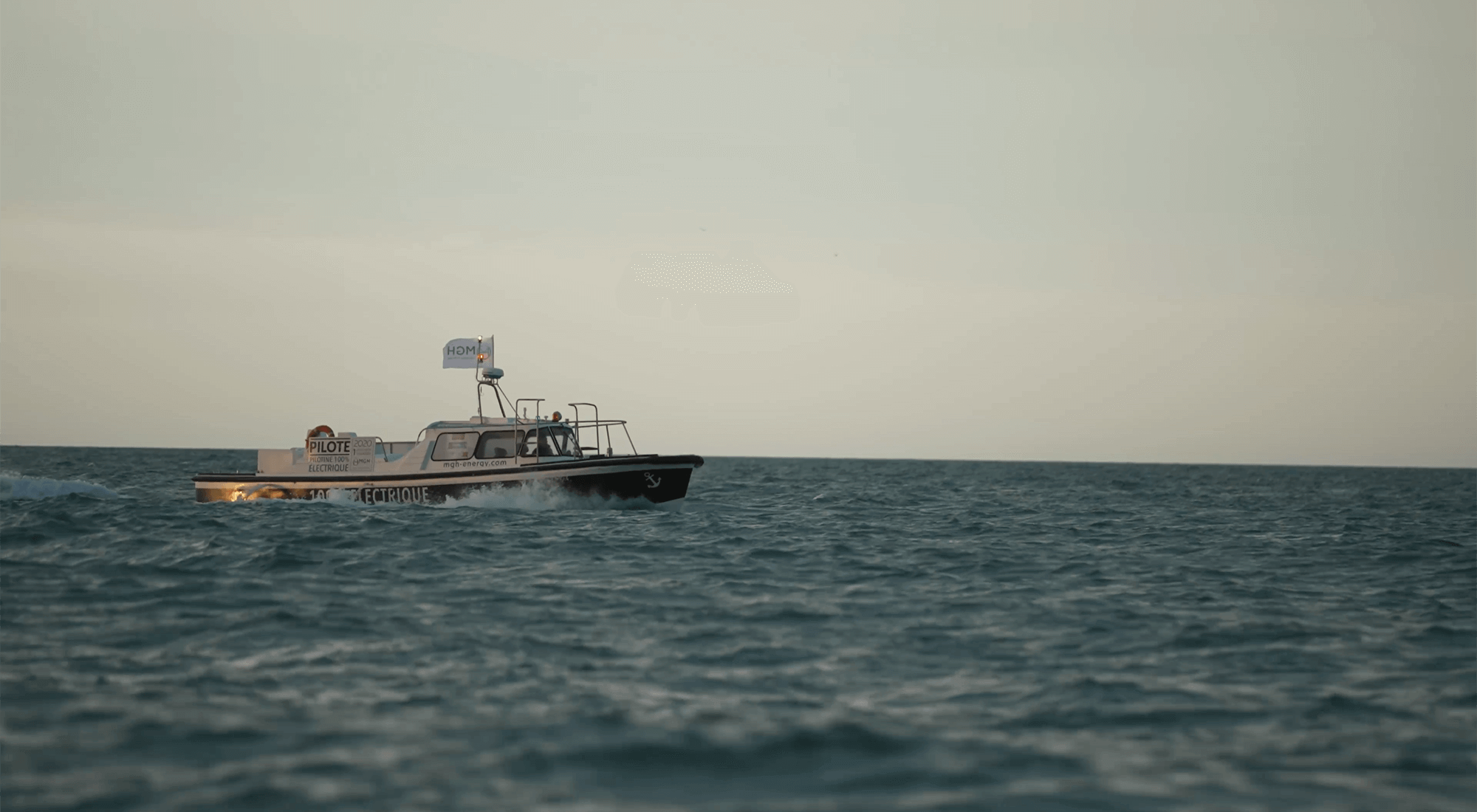
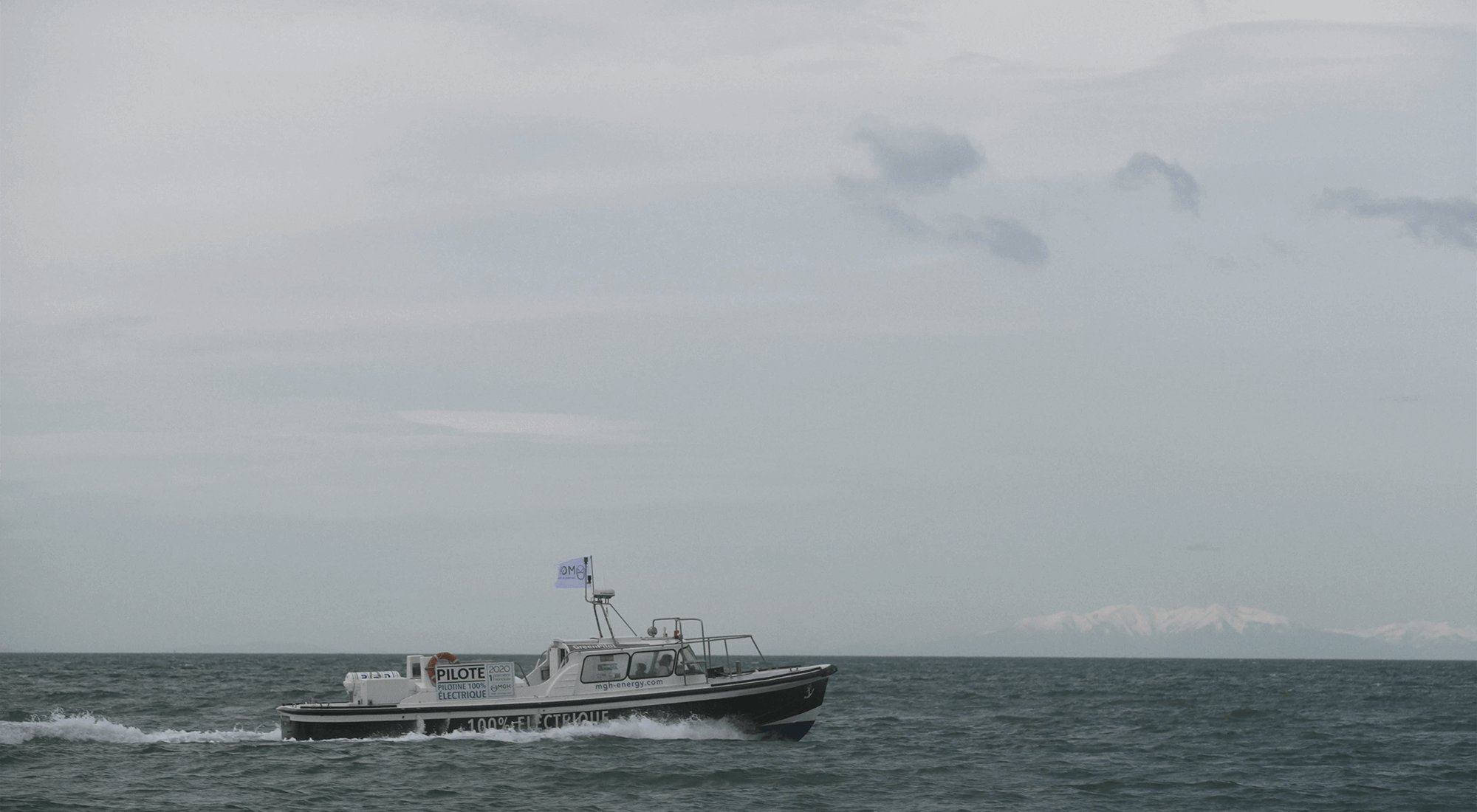
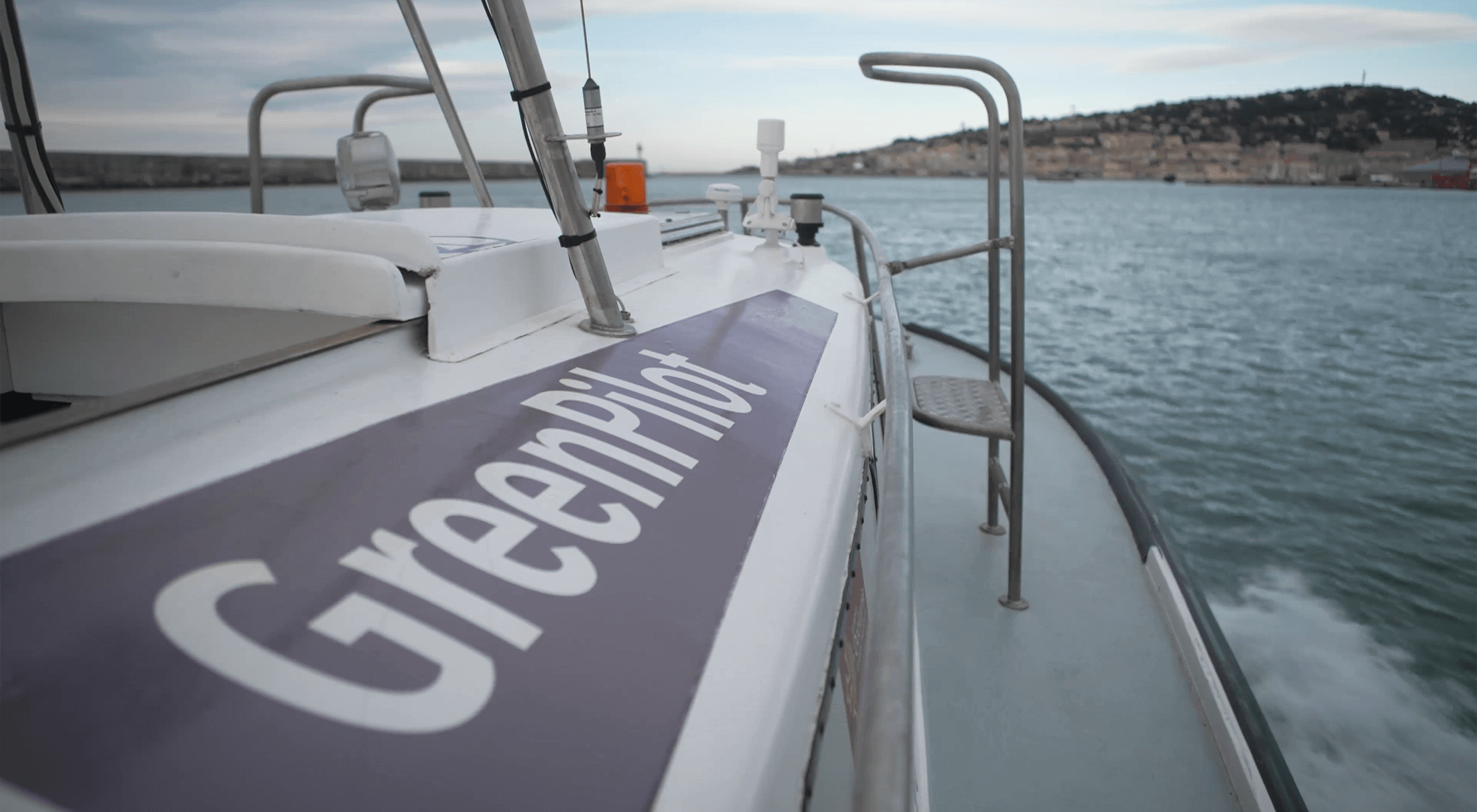
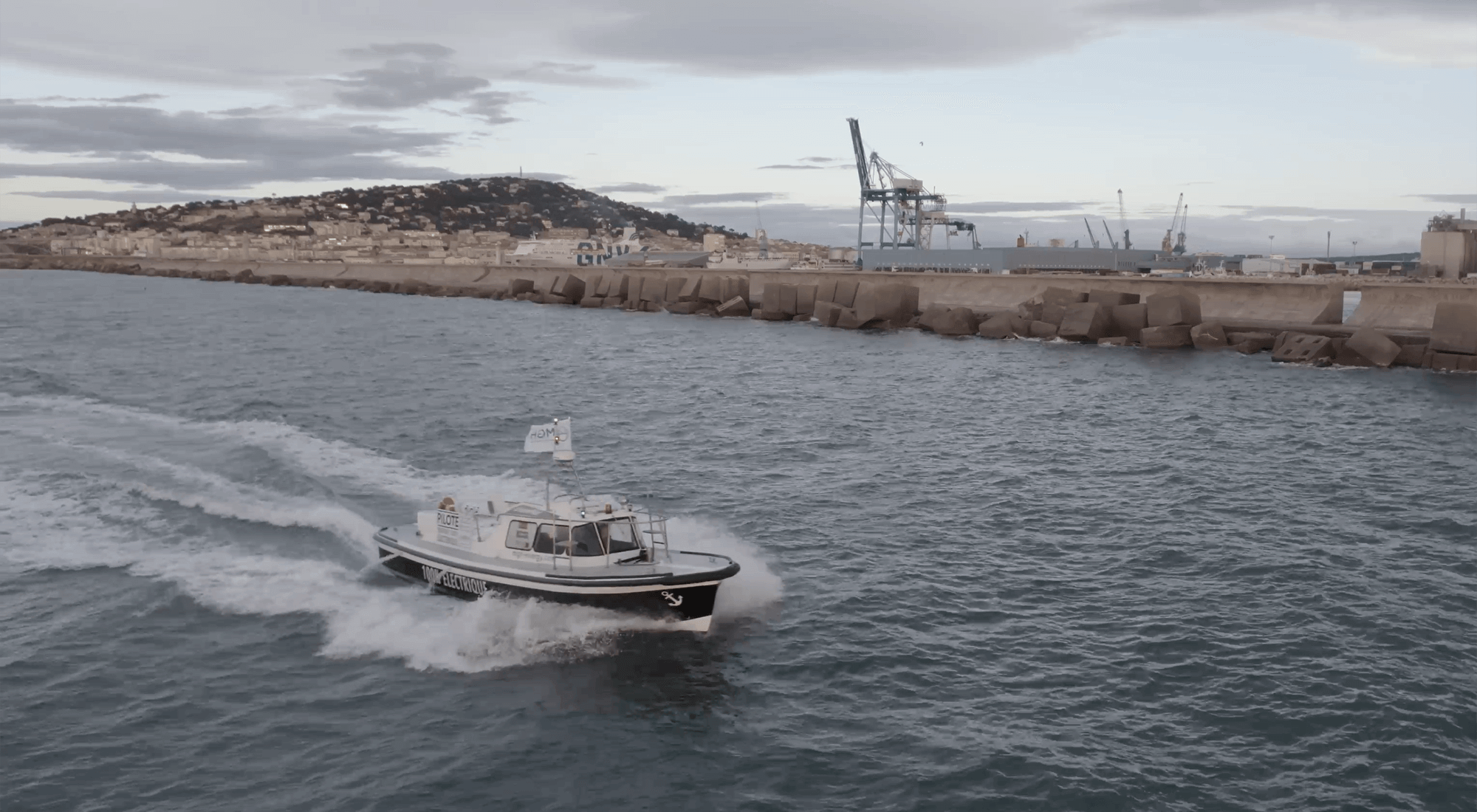
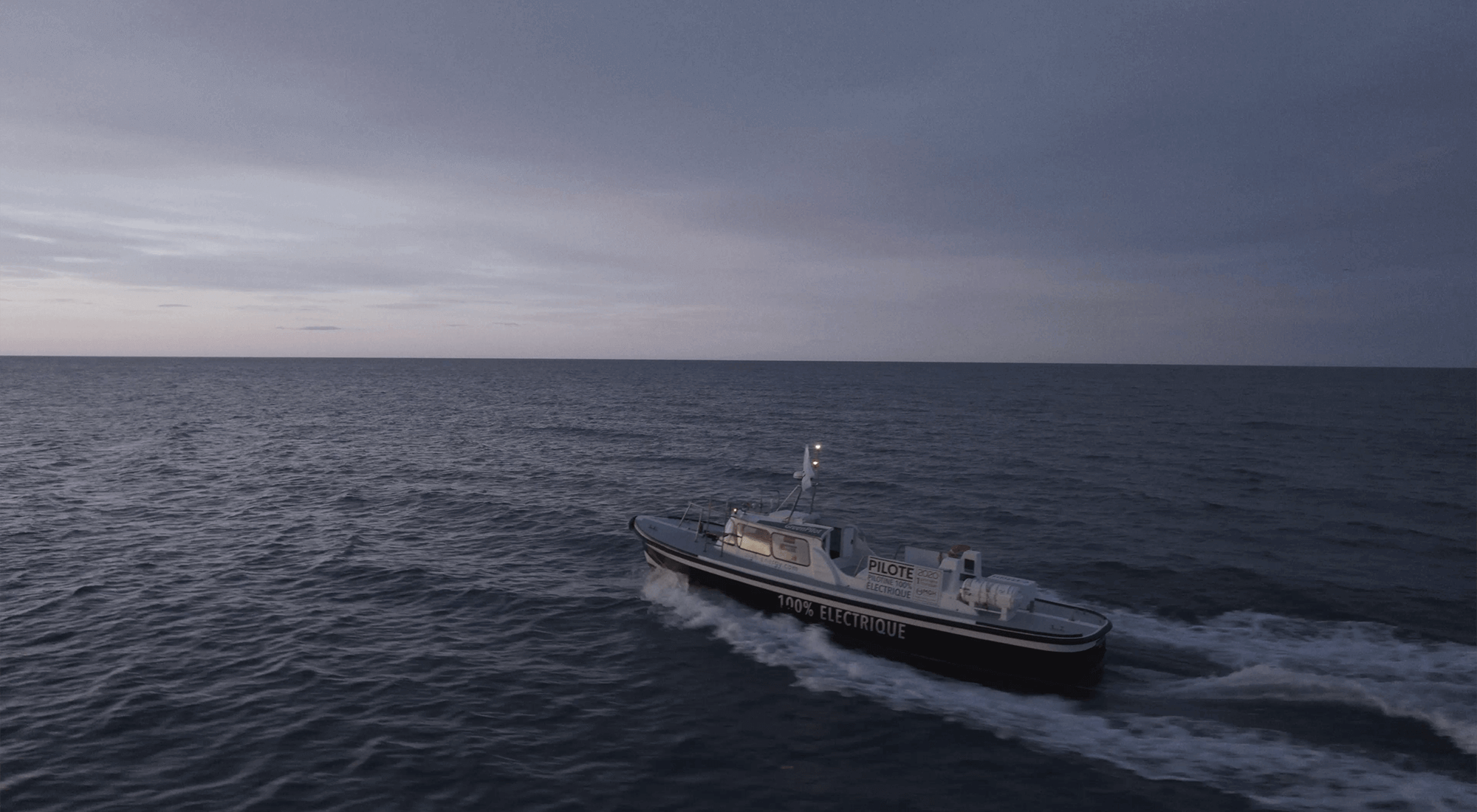
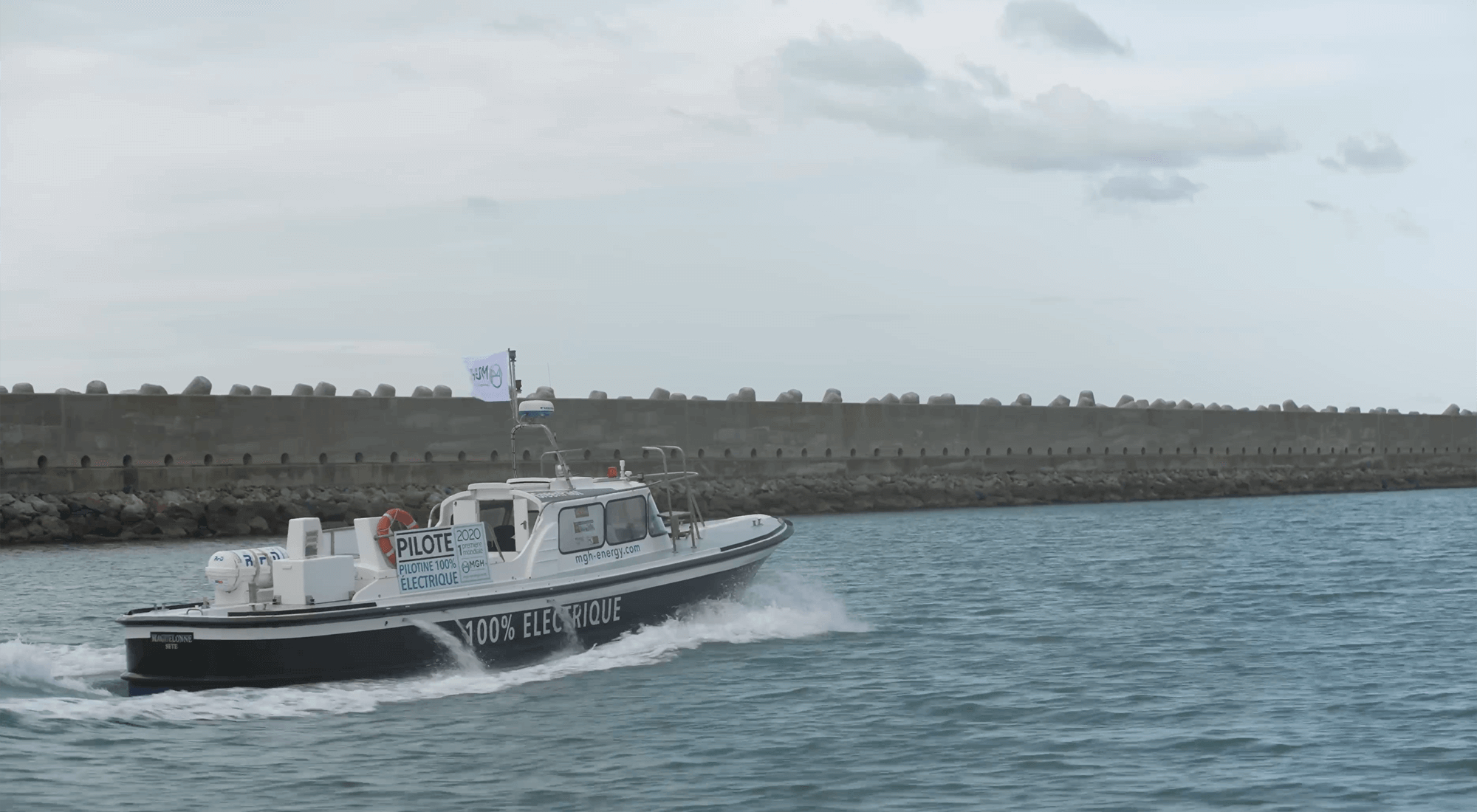
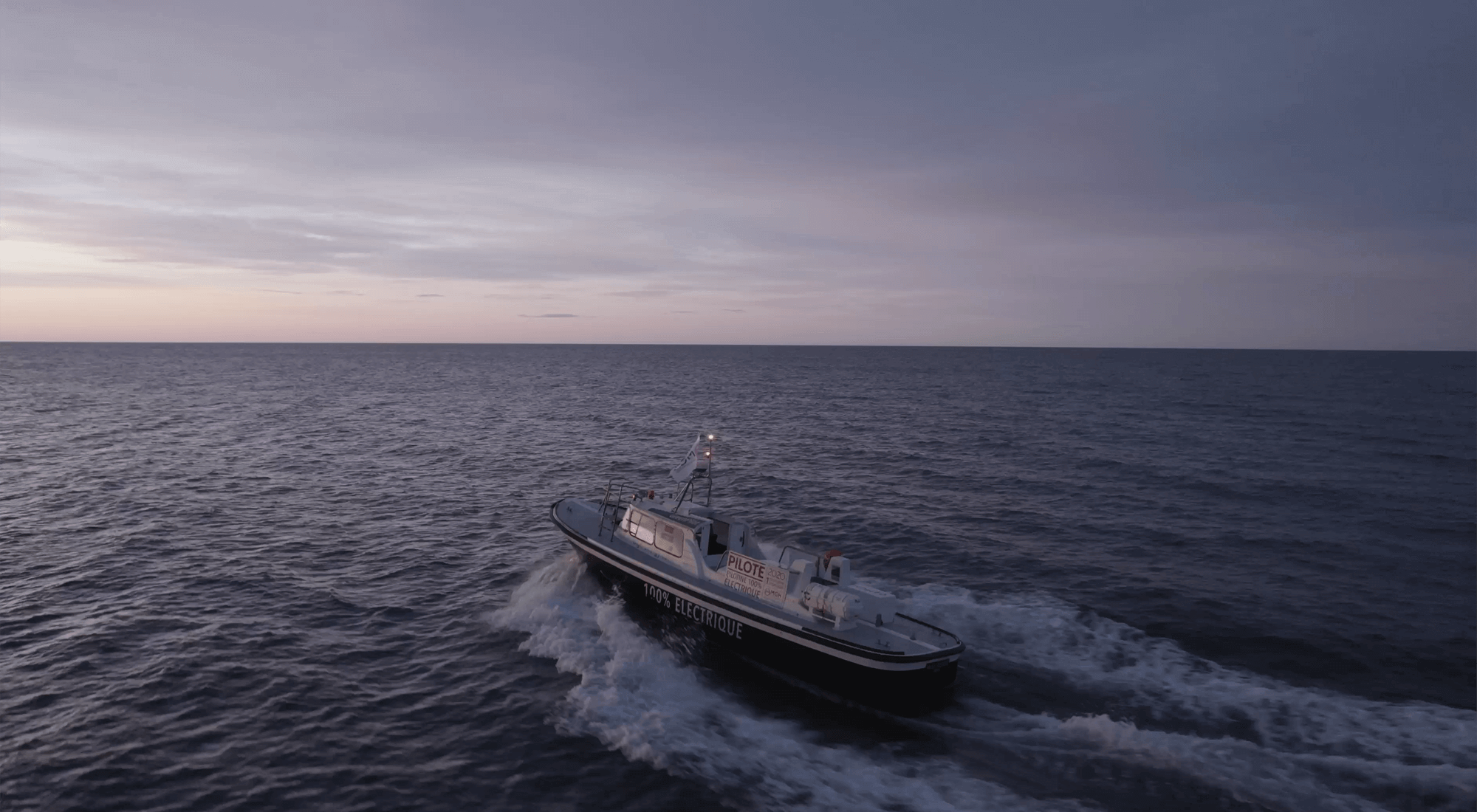
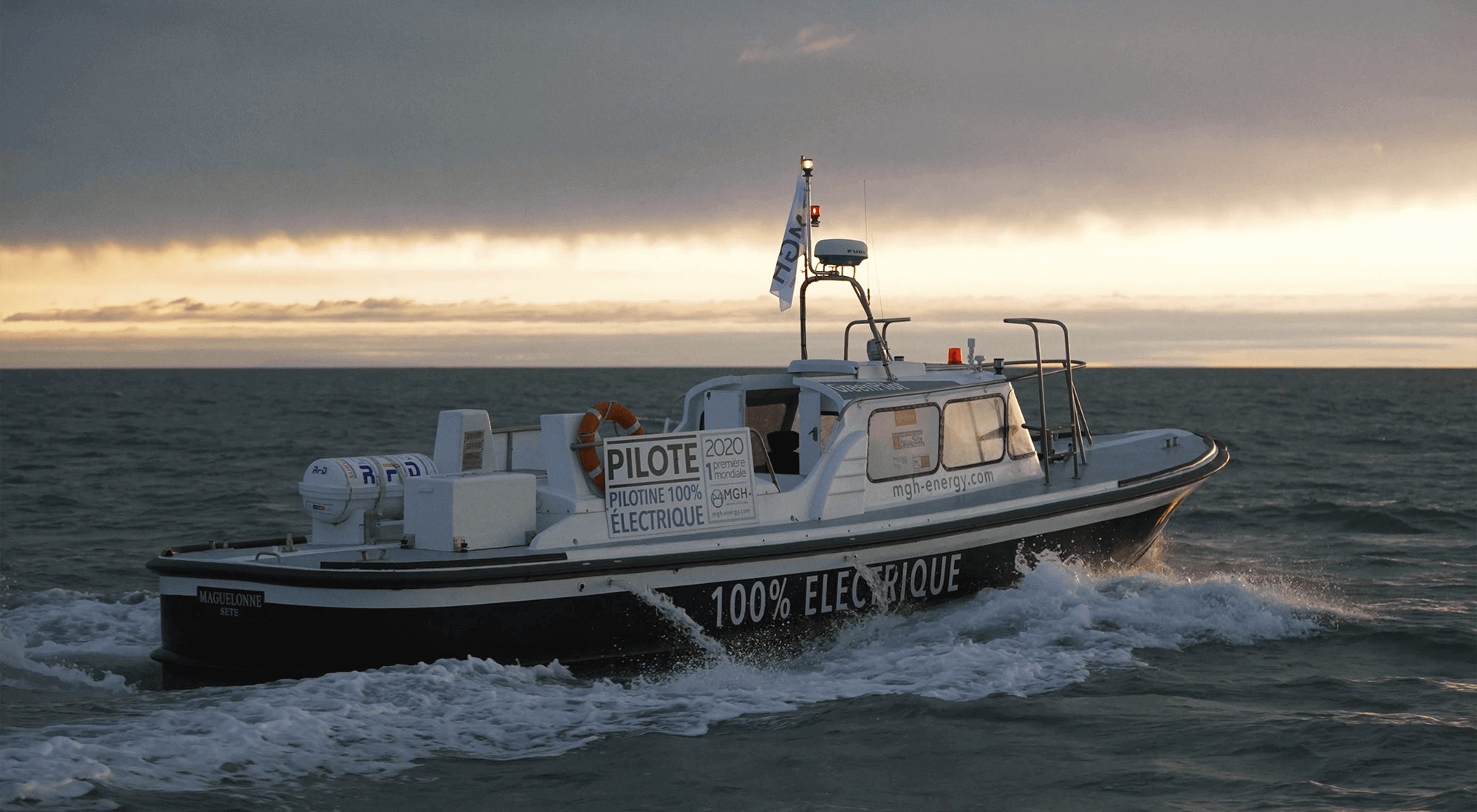
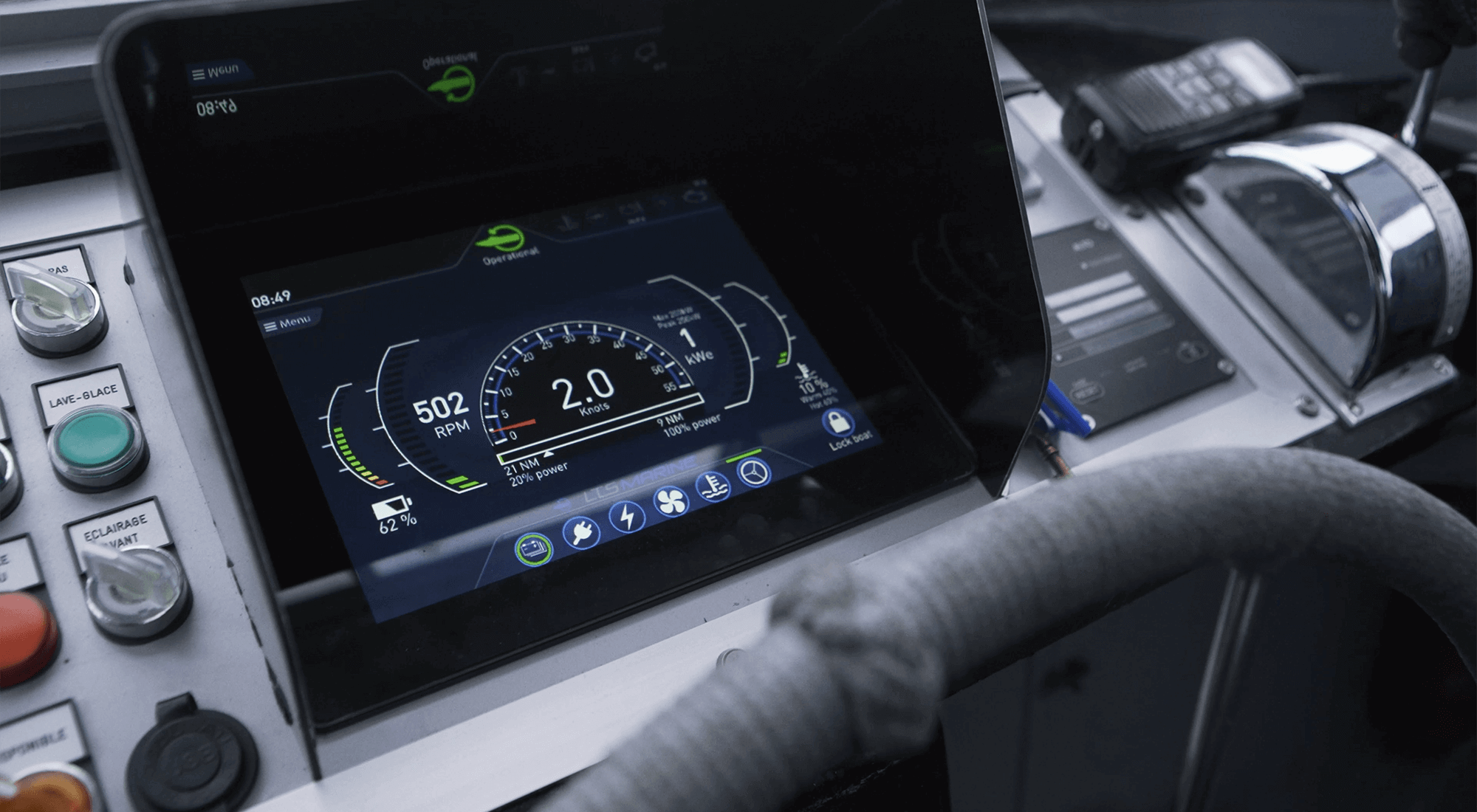
THE WORLD'S FIRST 100% ELECTRIC PILOT BOAT
With a 200kW electric motor powered by 6 onboard batteries, the e-Maguelonne is the world's first 100% electric pilot boat. Inaugurated in 2021, it is currently operated by the pilot vessels of the commercial port of Sète-Frontignan. The transformation of this pilot boat, which was initially powered by a combustion engine, gives the maritime industry the opportunity to take a further step towards decarbonising port activities.
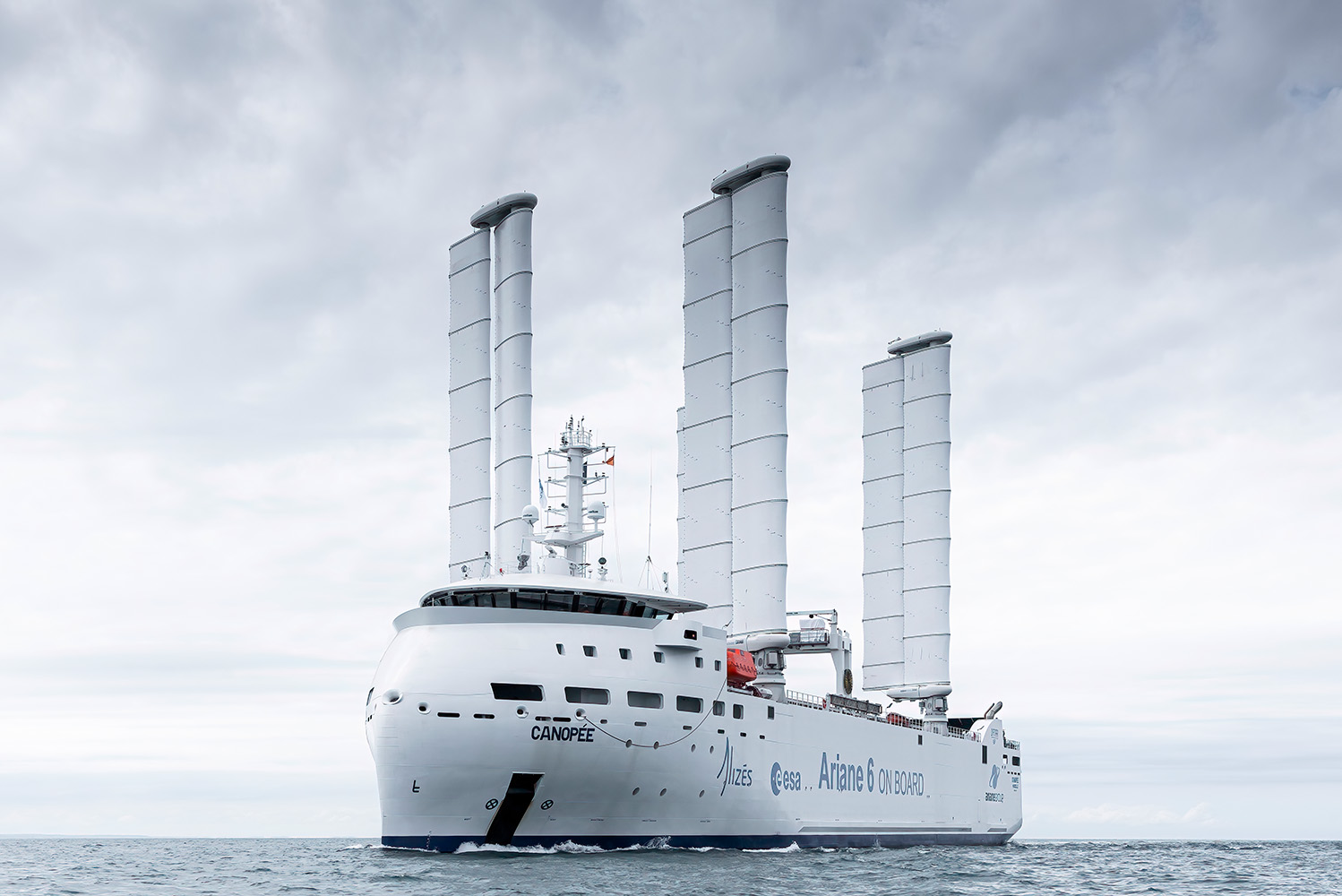

WIND-POWERED MARITIME TRANSPORT
As part of its maritime transport decarbonization strategy, MGH Energy acquired a 25% stake in the start-up Zéphyr & Borée in 2019. This shipping company designs and markets low-carbon maritime transport solutions on an industrial scale by combining wind propulsion, speed reduction, and the use of alternative fuels to fossil energy.
The company is notably behind the modern sail-powered cargo ship Canopée, developed in partnership with Jifmar to meet ArianeGroup's needs. It is also currently working on developing a transatlantic container transport line. With its "low-carbon" ship projects, Zéphyr & Borée is driving the development of more sustainable and responsible maritime transport.